
Cancer treatment has long been a challenging field, with researchers continuously seeking innovative methods to enhance therapeutic outcomes. Recently, a significant breakthrough has been made by a multidisciplinary team led by?Professors Gigi?P.-C.?Lo?and?Kwan T. Chow?from the Department of Biomedical Sciences at City University of Hong Kong. Their pioneering research, titled “Inducing Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death through Oxygen-Economized Photodynamic Therapy with Nitric Oxide-Releasing Photosensitizers,” has been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition?(with Impact Factor of 16.6;?2022 Journal Citation Reports, Clarivate, 2023).
Innovative Approach to Cancer Therapy
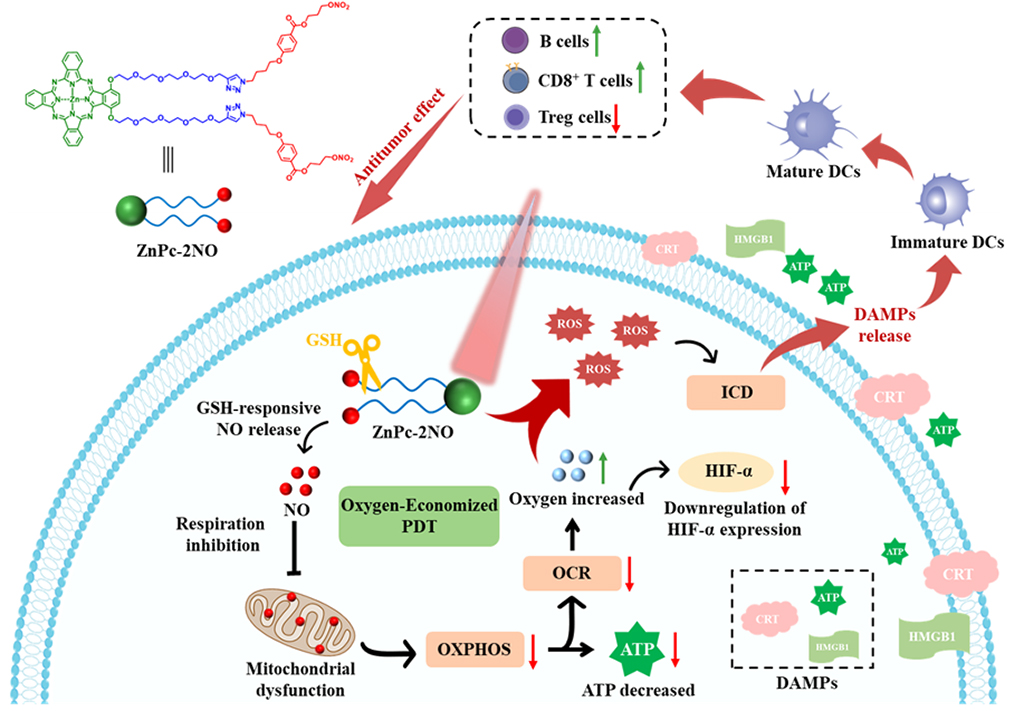
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a treatment that uses light-activated photosensitizers to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which kill cancer cells. However, its effectiveness is often limited by the availability of oxygen within tumors. To address this, Professors Lo and Chow’s team has developed a novel approach that economizes oxygen usage while simultaneously releasing nitric oxide (NO), a potent anti-cancer agent.
Their research introduces two zinc(II) phthalocyanines, ZnPc-2NO and ZnPc-4NO, which are substituted with nitric oxide-releasing moieties. These compounds suppress mitochondrial respiration, sparing more intracellular oxygen for PDT. This dual-action mechanism not only improves PDT efficiency by reducing its oxygen dependency but also stimulates the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively. The study demonstrates that this innovative therapy significantly inhibits tumor growth and induces a robust anti-tumor immune response in preclinical models.
Collaborative Efforts and Expertise
This groundbreaking study was conducted through the collaborative efforts of PhD students Feijie Xu, Meijun Wang, and Eunice Dotse, under the guidance of Professors Lo and Chow. The Lo’s lab designed and developed the novel photosensitizers, demonstrating their ability to release NO upon interaction with intracellular glutathione.?This reduces cellular oxygen consumption and alters mitochondrial membrane potential, effectively overcoming the hypoxic conditions of tumors and enhancing PDT efficacy.
Meanwhile, the Chow’s?lab investigated the efficacy of the therapy in mouse models, leveraging their expertise in tumor immunology. They demonstrated that ZnPc-2NO could trigger immunogenic cell death (ICD) and the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) in cancer cells, leading to the maturation of dendritic cells and the activation of a robust anti-tumor immune response.
Implications for Cancer Treatment
“Our study presents a novel strategy to enhance the efficacy of photodynamic therapy by incorporating nitric oxide-releasing photosensitizers,” stated Professor Lo. “This dual-action approach not only economizes oxygen usage but also induces immunogenic cell death, which can potentially transform the landscape of cancer therapy by leveraging the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively.”
The findings underscore the potential of integrating photodynamic therapy with immunotherapy, offering a promising new avenue for cancer treatment. By reducing the oxygen dependency of PDT and enhancing the immunogenicity of cancer cell death, this innovative approach could lead to more effective and durable therapeutic outcomes.
Future Directions
The team plans to further optimize the nitric oxide-releasing photosensitizers and explore their application in various cancer types. Additionally, they aim to collaborate with clinical partners to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this novel therapy in clinical trials, paving the way for its eventual translation into clinical practice.
“Inducing Immunogenic Cancer Cell Death through Oxygen-Economized Photodynamic Therapy with Nitric Oxide-Releasing Photosensitizers” is published in June 2024. Full text is available at:?https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/anie.202404561
This breakthrough represents a significant advancement in the field of cancer therapy, offering new hope for more effective treatments that harness the power of both photodynamic therapy and the immune system.
