Efficient, Systematic Genetic Analysis Helps Dissect Disease Inheritance
Many genetic variants have been found to have a linkage with genetic diseases, but the understanding of their functional roles in causing diseases are still limited. An international research team, including a biomedical scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU), has developed a high-throughput biological assay technique which enabled them to conduct a systematic analysis on the impact of nearly 100,000 genetic variants on the binding of transcription factors to DNA. Their findings provided valuable data for finding key biomarkers of type 2 diabetes for diagnostics and treatments. And they believe that the new technique can be applied to studies of variants associated with other genetic diseases.
The study was co-led by Dr Yan Jian, Assistant Professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences at CityU, Professor Bing Ren from the University of California San Diego and Professor Jussi Taipale from the University of Cambridge. Their findings were published in the prestigious scientific journal Nature, titled “Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants”.
“Based on our findings, we believe that our high-throughput experimental method can be applied in the study of different genetic diseases, including colorectal cancer and prostate cancer. It can help dissect the mechanism of the genetic inheritance of the disease and find the biomarkers for clinical diagnosis,” said Dr Yan.
Unveiling the roles of noncoding variants in diseases
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS), which investigate the entire genome, has been the most important strategy in finding the genes associated with complex genetic diseases. Researchers have found hundreds of thousands of genetic variants in association with human diseases and traits. But studies on the functions of these variants are still limited.
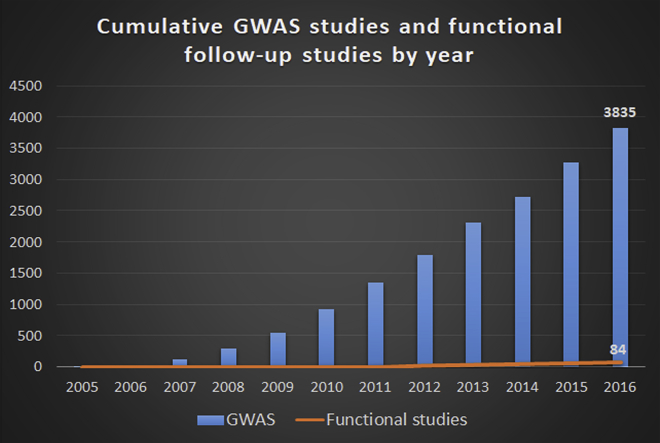
“Understanding the molecular functions of the noncoding variants will help us find out why people carrying these mutations are more susceptible to genetic diseases. This will help us develop methods or strategies to prevent, to detect or to cure the diseases early,” explained Dr Yan.
One of the variants’ functions is to affect the binding of transcription factors to DNA. The transcription factors will then control the gene expression in cells, turning the specific gene expression “up” and “down”, modulating the cellular functions.
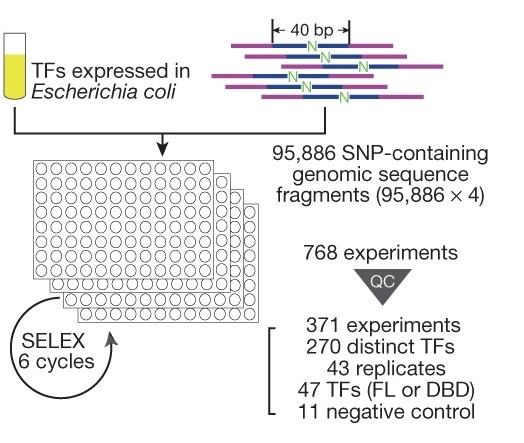
To systematically characterise the effects of genetic variants on the transcription factor binding, the team modified their previously developed experimental method into an ultra-high-throughput multiplex protein-DNA binding assay, HT-SELEX into an assay that can systematically and quantitatively evaluate the impact of a single nucleotide change on protein binding, termed “single-nucleotide polymorphism evaluation by systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment” (SNP-SELEX). Then they chose the genetic variants from the gene locations on the genome (called “gene loci”) that are known to be associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes as the object of analysis.
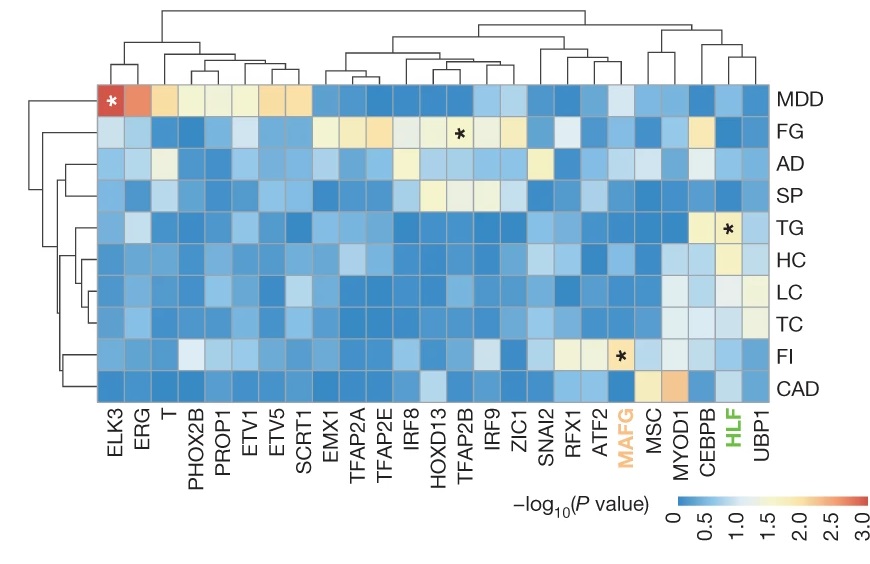
Utilising the SNP-SELEX, they successfully analysed the impact of 95,886 genetic variants on the binding of 270 distinct human transcription factors to DNA. They demonstrated that noncoding genetic variant SNP rs7118999 that increases the risk of type 2 diabetes can affect the DNA binding with one of the transcription factors, and the resulting molecular mechanism regulates the blood lipid level.
“This is a clear example of applying the data generated by SNP-SELEX that it can help identify the genetic variants which play key roles in the inheritance of type 2 diabetes. This would help the subsequent investigation in finding diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets,” said Dr Yan.
Speeding Up Analysis Significantly
Moreover, previous studies could only single out one or a few variants to find out its molecular mechanism. Each study took around 2-3 years. “So it was impossible to completely understand the complex genetic diseases like type 2 diabetes which are associated with hundreds of genetic variants within a short period. But with the SNP-SELEX, we could systematically analyse approximately 100,000 variants within a much shorter timeframe,” said Dr Yan.
“In this study, we only covered a relatively small portion of variants and transcription factors. So we will expand our study. By utilising the SNP-SELEX, hopefully it will help us uncover the underlying mechanisms of more and more of these noncoding variants very soon,” said Professor Ren.
Dr Yan, Dr Qiu Yunjiang from the University of California San Diego and Dr André M. Ribeiro dos Santos from the Federal University of Pará in Brazil are the paper’s co-first authors. Dr Yan, Professor Ren and Professor Taipale are the co-corresponding authors. Other team members include researchers from Karolinska Institutet, University of Cambridge, University of California San Diego and CityU, coming from US, UK, Sweden, Brazil, China and Hong Kong.
DOI number: 10.1038/s41586-021-03211-0
Related story: Regulatory mechanisms of virulence of a plant bacterial pathogen unveiled facilitating the development of new anti-bacterial drugs