CityU researchers develop an additive to efficiently improve the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells
Perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) are a promising alternative to traditional silicon-based solar cells because of their high power-conversion efficiency and low cost. However, one of the major challenges in their development has been achieving long-term stability. Recently, a research team from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) made a breakthrough by developing an innovative multifunctional and non-volatile additive which can improve the efficiency and stability of perovskite solar cells by modulating perovskite film growth. This simple and effective strategy has great potential for facilitating the commercialisation of PVSCs.

Credit: City University of Hong Kong
“This type of multifunctional additive can be generally used to make different perovskite compositions for fabricating highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. The high-quality perovskite films will enable the upscaling of large-area solar panels,” explained Professor Alex Jen Kwan-yue, Lee Shau Kee Chair Professor of Materials Science and Director of the Hong Kong Institute for Clean Energy at CityU, who led the study.
PVSCs have attracted significant attention due to their impressive solar power conversion efficiency (PCE). Since perovskites can be deposited from solutions onto the fabrication surfaces, PVSCs have the potential to be applied in building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), wearable devices, and solar farm applications. However, the efficiency and stability are still affected by the severe energy loss associated with defects embedded at the interfaces and grain boundaries of the perovskites. Therefore, the intrinsic quality of perovskite film plays a critical role in determining the achievable efficiency and stability of PVSCs.
Although many previous research studies have focused on improving the film morphology and quality with volatile additives, these additives tend to escape from the film after annealing, creating a void at the perovskite-substrate interface.
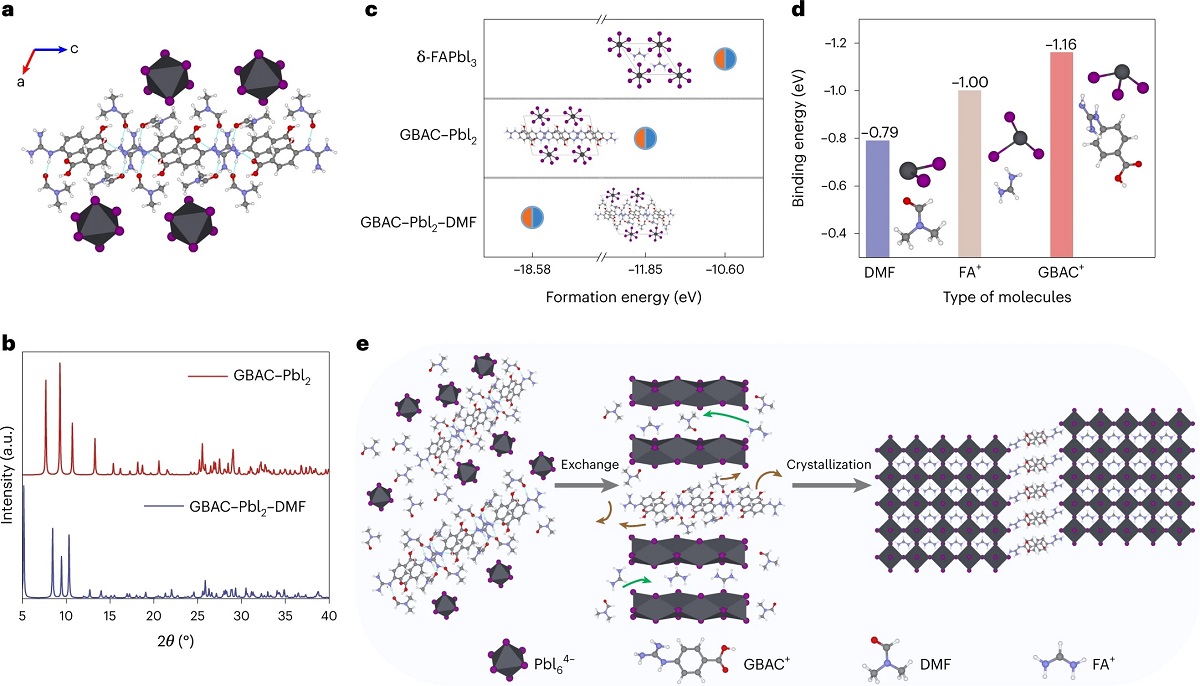
Photo credit: ? Li, F. et al., https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-023-01180-6
To tackles these issues, the CityU researchers developed a simple but effective strategy of modulating the perovskite film growth to enhance the film quality. They found that by adding a multifunctional molecule (4-guanidinobenzoic acid hydrochloride, (GBAC)) to the perovskite precursor, a hydrogen-bond-bridged intermediate phase is formed and modulates the crystallization to achieve high-quality perovskite films with large perovskite crystal grains and coherent grain growth from the bottom to the surface of the film. This molecule can also serve as an effective defect passivation linker (a method to reduce the defect density of perovskite film) in the annealed perovskite film due to its non-volatility, resulting in significantly reduced non-radiative recombination loss and improved film quality.
Their experiments showed that the defect density of perovskite films can be significantly reduced after introducing GBAC. The power conversion efficiency of inverted (p-i-n) perovskite solar cells based on the modified perovskites was boosted to 24.8% (24.5% certified by the Japan Electrical Safety & Environment Technology Laboratories), which is among the highest values reported in the literature. Also, the overall energy loss of the device was reduced to 0.36 eV, representing one of the lowest energy losses among the PVSC devices with high power conversion efficiency.
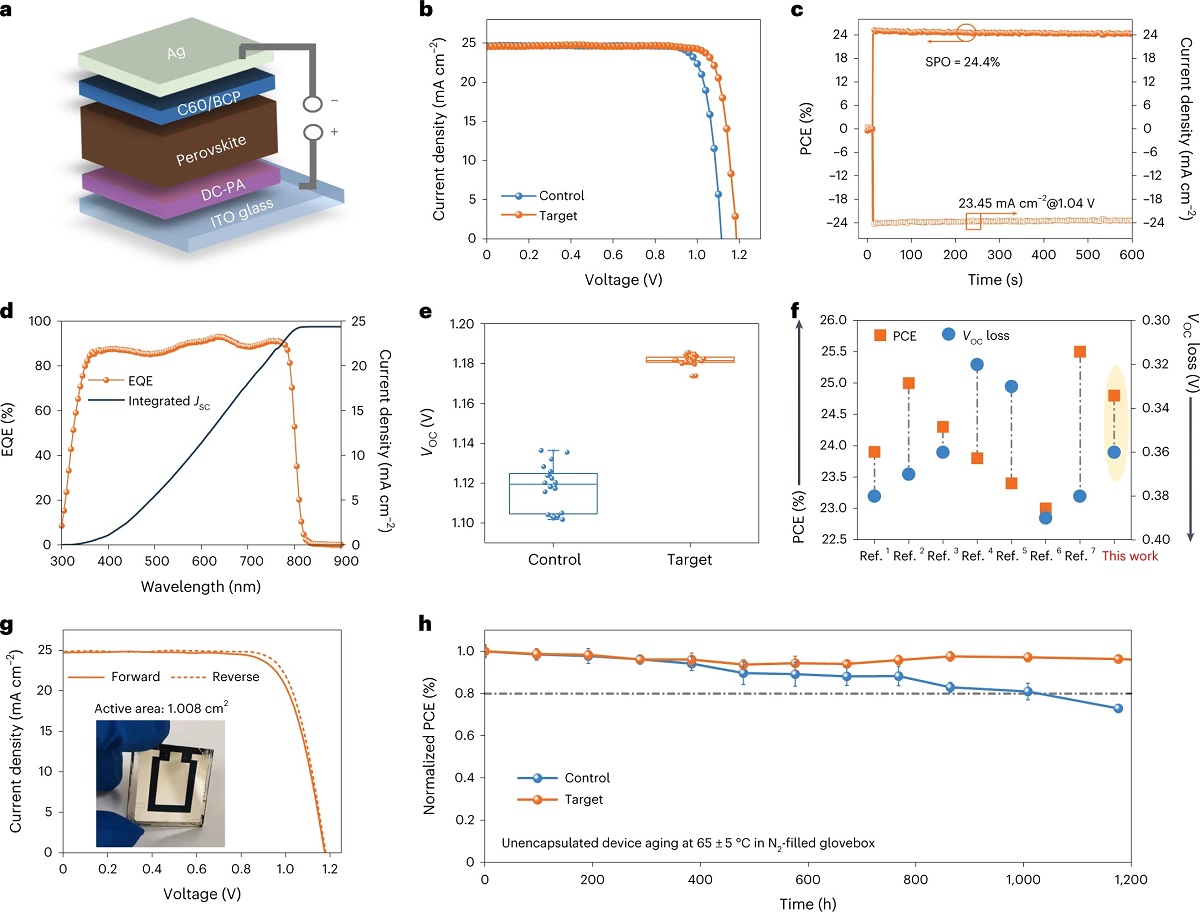
Photo credit: ? Li, F. et al., https://www.nature.com/articles/s41566-023-01180-6
Additionally, the unencapsulated devices exhibit improved thermal stability beyond 1,000 hours under continuous heating at 65 ± 5 °C in a nitrogen-filled glovebox while maintaining 98% of the original efficiency.
The team demonstrated the general applicability of this strategy for different perovskite compositions and large-area devices. For example, a larger area device (1 cm2) in the experiment delivered a high PCE of 22.7% with this strategy, indicating excellent potential for fabricating scalable, highly efficient PVSCs.
“This work provides a clear path to achieving optimised perovskite film quality to facilitate the development of highly efficient and stable perovskite solar cells and their upscaling for practical applications,” said Professor Jen.
In the future, the team aims to further extend the molecular structures and optimize the device structure through compositional and interfacial engineering. They will also focus on the fabrication of large-area devices.
The findings were published in the scientific journal Nature Photonics under the title "Hydrogen-bond-bridged intermediate for perovskite solar cells with enhanced efficiency and stability."

Credit: City University of Hong Kong
Professor Jen is the corresponding author of the research. The co-first authors are Miss Li Fengzhu and Dr Deng Xiang from Professor Jen’s research group. Other team members from CityU include Dr Chen Xiankai, Dr Tsang Sai‐wing, Dr Yang Zhengbao, Dr Francis Lin and Dr Wu Shengfan.
The research was supported by CityU, the Innovation and Technology Commission, the Research Grants Council, the Green Tech Fund of the Environment and Ecology Bureau in Hong Kong, the Guangdong Major Project of Basic and Applied Basic Research, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Joint Laboratory of Optoelectronic and Magnetic Functional Materials.